Our country pages
Africa
Europe
Search
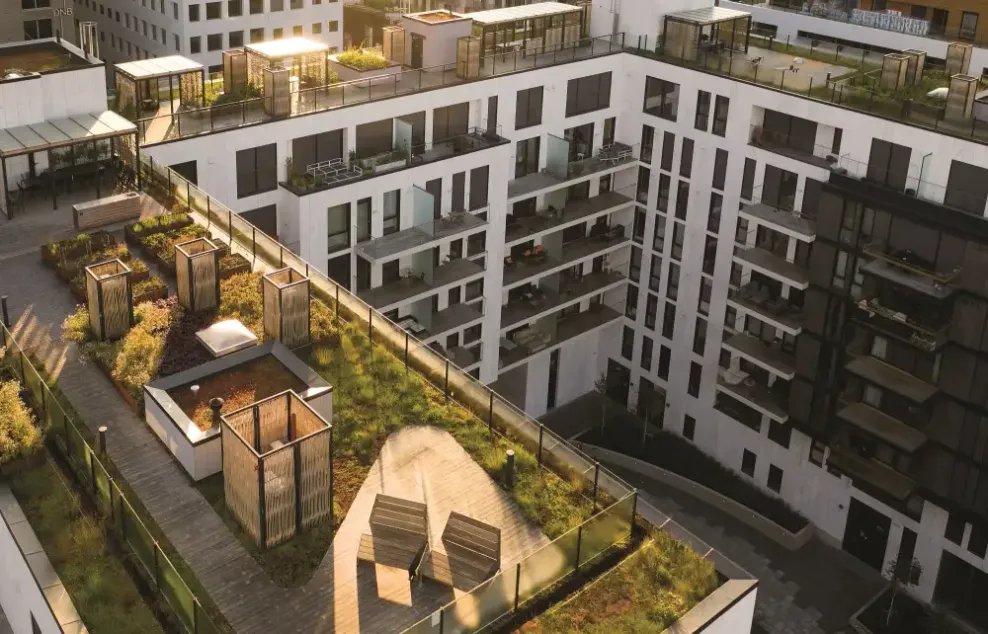
Greener in the city with flat roofs

Share article:
Flat roofs and green roofs
Continuous roofing, or flat roofs are much more common in urban areas than one might think.
They complete many multi-family buildings, extensive low buildings used as garages or for commercial and industrial functions.
They conclude more contemporary residential buildings or we observe them in those Italian locations historically characterized by past Arab influences.
Without going into the solutions defined for the tertiary sector and concentrating on the residential sector, we can make a few considerations and observe how these spaces are often deprived of a use function, as well as being abandoned, dirty and unpleasant. Many times, they are also concluded by bituminous waterproofing that creates large dark surfaces, which attract heat and contribute to local overheating.
Jump to section
Flat roofs and green roofs
Continuous roofing, or flat roofs are much more common in urban areas than one might think.
They complete many multi-family buildings, extensive low buildings used as garages or for commercial and industrial functions.
They conclude more contemporary residential buildings or we observe them in those Italian locations historically characterized by past Arab influences.
Without going into the solutions defined for the tertiary sector and concentrating on the residential sector, we can make a few considerations and observe how these spaces are often deprived of a use function, as well as being abandoned, dirty and unpleasant. Many times, they are also concluded by bituminous waterproofing that creates large dark surfaces, which attract heat and contribute to local overheating.
Green Flat Roof
The advantages of green flat roofing
The overhaul of these sometimes very large spaces can yield truly interesting solutions, both in terms of function, aesthetics and microclimate; let's look at the main ones. If we look at the functional aspects, the green roof:
- achieves a kind of “green compensation”: every building leads to the subtraction of natural land, an operation that should be limited and that has led to specific regulatory guidelines in terms of reducing soil consumption. The moment a green roof is created, what has been taken away is, in some way, reintroduced;
- Especially in some valuable contexts, the so-called “green roof” has an aesthetic mitigation function: it is suggested and sometimes rewarded by those more far-sighted local administrations, since it helps to improve the aesthetic appearance of spaces such as garages and underground car parks and to reduce their visual impact;
- Today, more than ever, in this post-pandemic era, we have all realised the importance of having a private outdoor space: an outlet outside for our children to play and enjoy the good weather.
- The flat roof of our homes provides us with an extra functional green space, which is of course adequately protected and fitted with parapets that comply with standards; the roof can serve a productive function: the urban vegetable garden, a beautiful and practical solution for self-producing zero-mile fruit and vegetables; it is fun and educational, as it teaches our children how to grow plants and flowers.
Green roofs: solutions that support living comfort and provide well-being
The green flat roofing represents a truly environmentally friendly intervention, as it ties in with the themes of energy efficiency and the use of renewable resources.
Here, in summary, are some arguments in favour of flat green roofing:
- manages rainwater on the roof by reducing its velocity and allowing a more controlled runoff that does not undermine gutters and downpipes
- stores rainwater and returns some of it to the atmosphere, making a significant contribution especially during the driest times of the year
- produces thermal mitigation, cooperating in winter insulation and cooling in summer
- contributes in terms of energy improvement and as such is linked to the issue of tax deductions
- can become home to photovoltaic systems, strongly incentivised by current environmental and fiscal policies
- filters fine dust and particles
- absorbs sound waves and reduces electrosmog
- represents a new living environment for vegetation and small (but valuable) animal communities in the city
- increases the value of the property
The flat roof connects our building to the surrounding landscape, enhancing it perceptually and creating a piece of the urban green system. It is not just an element of beautification but a further step towards long-term resource management and environmental and ecological protection.
BMI Academy has been offering seminars for designers and raising awareness among students of Construction, Environment and Territory Institutes on these innovative roof types for some time now; and as it did recently through specific webinars, it will continue to emphasise their functionality.
Discover BMI Expert
Discover BMI Expert
If you have a project to implement, you can ask the BMI Expert team for technical support. You will be able to discuss the best solution for your design needs while also receiving a technical brochure.

FAQ about Green Roofing
What is a green roof?
A green roof is a flat or sloping roof covered with vegetation. When building a green roof, it’s important to think about its composition, which must be made up of layers of different but interacting materials to ensure
- water accumulation
- water tightness
- protection against root action
- mechanical protection
- draining and filtering activity
- nutrients get to the plants.
Are green roofs eco-friendly?
Green roofing has a lot of benefits when it comes to dealing with sustainability, the environment and climate change concerns, particularly smog and pollution. These benefits include
- encouraging wildlife: rooftop habitats can provide a 'green link' that connects natural pockets of habitat to each other. They can also provide isolated habitats that are not disturbed by other green areas at ground level
- improving air quality: green roof plants improve air quality by absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
- improving temperature regulation: through the daily cycles of condensation and evaporation, plants are able to cool and humidify the surrounding air, improving the microclimate
- reducing and slowing stormwater runoff: in urban areas in certain climates, green roofs can retain nearly all storm-related water during the summer months, and up to 20% during the winter months.
What are the best plants to use on a green roof?
It is often best to plant species on a green roof that require minimal maintenance. Vegetation composed of sedum essences can survive extreme drought and easily regenerate and self-propagate.
Green roof design can also include Blue Green Roof technology, which offers all the performance features typical of green roofs while offering the possibility of storing, conserving and reusing rainwater. It is also a useful solution for reducing the effects of extreme rainfall that can cause localised damage.
What is the most eco-friendly roofing material?
When it comes to choosing roofing materials, strong, durable and - more recently - eco-friendly characteristics are most often selected. These traits are available in both materials and solutions. For example:
- wooden shingles: these are shingles made from shredded wood from controlled forests
- slate and clay roof tiles: terracotta roof tiles are made from porous ceramic with clay as its base. Clay is a natural material and has been used in the building process for centuries due to its durability and low maintenance
- solutions with unique characteristics: such as Noxite bituminous waterproofing membranes, which not only provide a high-quality flat roof, but reduce pollution by using the sun to transform harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) into harmless nitrates, which are washed away by the rain. Noxite is a highly effective means of reducing the ongoing environmental impact of a building as it continues to function throughout the life of the roofing membrane
- green roofs: the green roof solution reduces the heat island effect, boosts the insulation capacity of the environment below and improves air quality
- cool and white roofs: these reduce roof radiation by reducing overheating and so the air conditioning required.
Are green roofs expensive?
The price of a green roof depends on the size of the roof, the steepness or pitch, the type of green solution chosen and the vegetation planted. When considering the cost, remember to take into account the benefits of green roofs as a source of clean air, emotional wellbeing and environmental diversity.
If you’re investing in a green roof, it’s important to know exactly what the benefits are so that you get a great return on investment:
- roof membrane protection: vegetation on a roof deck protects the roof surface from the extremes of weather, temperature and UV radiation, which can significantly increase its lifespan
- reduced storm water run-off: water is stored by the green roof substrate and then taken up by the plants, where it is returned through transpiration and evaporation into the atmosphere. The drainage layer in green roofs also delays the rate at which water run-off occurs, reducing stress on drains and sewers during heavy rainfall
- reduced energy costs: the layers of a green roof system improve the thermal performance of the roof, helping to keep the rooms below cool in summer and warm in winter (although this effect is generally not included in any U-Value calculations).
How long do green roofs last?
Green roofs can extend the life cycle of a roof for more than 30 years as its layering makes it more durable than normal roofs. It is important, though, that the membrane and the stratigraphy (or layers) are correctly installed.
How long does a flat roof last?
A flat roof usually has an average lifespan of about 15 years. Many of its components require maintenance from time to time and, if this is not done, the roof can be damaged by infiltration. To make the roof last as long as possible, it is important to carry out frequent inspections and work on the drainage system.
How frequently should roof maintenance be performed? And what does this involve?
The health of the roof changes over time depending on the attention you give it. To ensure high quality roof products remain fully functional over decades, it is essential to follow a regular maintenance programme.
Maintenance problems normally include infiltration, cracks in the roof covering or tiles, deterioration of the membranes and insulation. If not repaired, the roof's insulating performance will decline.
Inspect your roof after storms and high winds, and at major discontinuity points, and clean it periodically.
And remember to check your product’s warranty, whether you have installed just a few tiles or an entire roof system. A good warranty can protect you from costly repairs in the future.
How do you install a green roof?
A green roof is a surface that needs to be made waterproof to avoid damage from water seeping in. So, it is essential to have an anti-root membrane and a draining layer that will help carry away excess water from the rain or gutters.
Then, adding a drainage mat and felt layer will allow the water to pass through and the roots to attach themselves to the growing medium. The drainage layer will then provide the growing platform for the green roof. The composition of the soil is also important as it aids proper plant nutrition and growth.
Finally, the roof must include an irrigation system, possibly water-based, so as not to overload the roof, and reduce water consumption and waste.
If you choose an intensive green roof, you can plant classic garden plants, both herbaceous and shrubs. If you opt for an extensive green roof, low-lying and creeping plants are best as they are suitable for growing in thin layers of substrate.
What is a blue roof and why is it considered environmentally friendly?
A blue roof can be key to sustainability in buildings, particularly in urban areas where a ground level solution may not be possible due to lack of space. Benefits of a blue roof include
- temporarily store rainfall to reduce runoff
- reduce the flow rate of water from the roof
- store water for reuse in other areas of the building, such as irrigation or cooling
- make up the drainage and support layers for green roofs
- Easy to maintain.
If your business is located in an area particularly prone to flooding, then a blue roof system can also help to protect your building (and neighbouring ones) from damage.
Contact Us
Contact our local team
We can support you to define solutions and services for specific country.
Media Contact
Contact us for more information on BMI Group
group.communications@bmigroup.com